
By partnering with Request Network, Wikimedia France is able to reap the following benefits of blockchain technology.
• Simplicity and security
• Transparency of donations and trust
• Traceability of funds raised
• Lower transaction costs
• Speed of transactions
• Financial inclusion
Donors no longer need to be worried about funds being accessed by third parties. Furthermore Wikimedia will be readily available for disbursement to important projects, thereby enabling the company to avoid crisis situations.
Wikimedia is not the frontrunner in accepting cryptocurrency payments. Fidelity Charitable started accepting digital payments back in 2015. However, by integrating Request Network’s plugin, Wikimedia will practically accept any cryptocurrency.
Payment plugin
Request network also announced the release of the first decentralized payment plugin for WooCommerce — powered by Request Network. The facility enables any user of WooCommerce to accept cryptocurrency payments. The plugin is offered for free and has no hidden fees. It can be integrated with any eCommerce platform easily.
WooCommerce is currently the most popular eCommerce platform on the web and commands approximately 42% of the total market share for platforms used by all the eCommerce websites.
About Request Network
Request Network is a decentralized network, which allows anyone to request a payment (a Request Invoice), where the recipient is able to pay in a secure way and all the information is stored in a decentralized authentic ledger.
Anyone can write on the Request Ledger and create a Request for Payment. The Request can be detected by the recipient monitoring the network (via a wallet or via a financial application). If the request is approved by the user, it can be paid with a single click. Then the request is completed and the network is updated.
This results in cheaper, easier and more secure payments and allows a wide range of automation possibilities on top of it. The platform is built on the Ethereum blockchain.
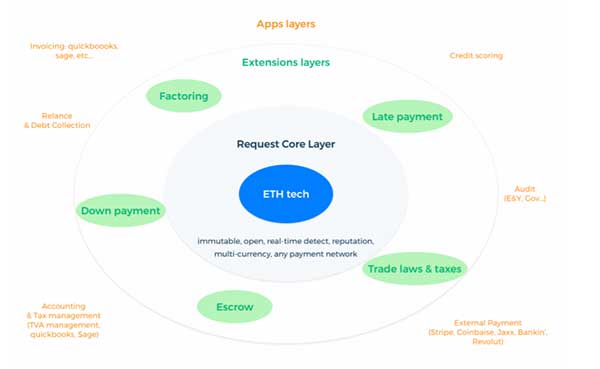
Request Network consists of three layers:
Core layer – The bottom layer is the Core, which manages the consensus over the ledger and the state transitions. It consists of the most fundamental smart contracts, allowing the creation of different entities and requests for payments. It also detects when payments have been completed.
Extension layer – Most payment requests created today are not as basic as the one proposed by the Core layer. If the request comes from an enterprise, then it includes rules for calculating taxes, payment terms, escrows or advances. All of these conditions take the form of available extensions that can be added to requests. This layer is the gateway to incredible features that do not yet exist, such as ”continuous bills.” For example, someone could choose this module to break down their rent into 30×24 payments to the landlord, leaving this person with a fluid bank account without large end-of-month expenses. Taxes would be rerouted in real time to government agencies. With each payment, 20% of VAT would go to taxes and 80% to the recipient company. The same example would allow everyone to give 1% of all payments to NGOs (Non Governmental Organizations), or to deposit them into ones own retirement account.
Application layer – The topmost layer is the Applications layer, which takes place outside the blockchain. Systems from different companies can connect to Request to create requests or access information. Accounting, audit, tax, debt recovery and collection, factoring or payment systems can all be connected. When a payment system connects to Request (Mycellium, Coinbase, Bank of America,etc.,), it will be able to access the invoices of the user and propose to pay them instantly. The Request team will develop applications, including an interface and an API for creating and accessing requests.
Request Network is backed by venture Capital giant Y Combinator. Request Network, by virtue of its reliability and versatility, is often referred to as PayPal 2.0.
